Investigation of boundary effects imposed by different types of centrifuge containers
Centrifuge experiments are considered ideal benchmarks when validating numerical models. However, such models are installed in (rigid or flexible) model containers. Read more...
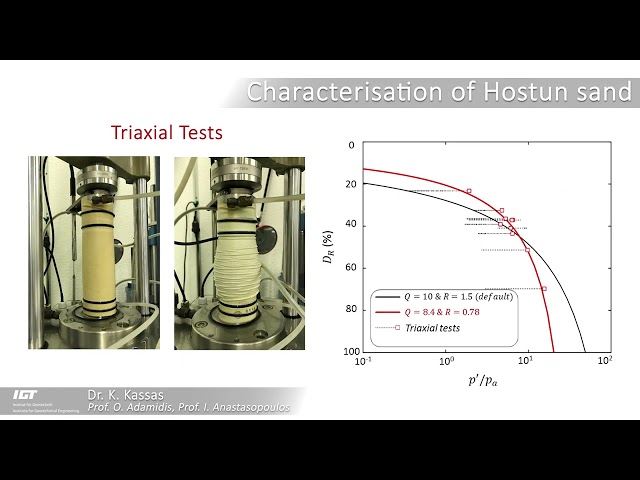
Centrifuge experiments are considered ideal benchmarks when validating numerical models. However, such models are installed in (rigid or flexible) model containers. How important are boundary effects? To answer this fundamental question, we numerically investigate the influence of different types of centrifuge containers on shallow foundations subjected to liquefaction. Boundary effects are minimized with a laminar container, where a normalized boundary distance L/DL ≥ 1 is found to be adequate for all liquefiable layer depths (DL) examined. The use of a rigid container is proven problematic, as it always imposes an unrealistic wave propagation pattern. The use of Duxseal inclusions offers a major advantage, allowing accurate reproduction of foundation settlement even with L/DL ≥ 1, a key conclusion for the design of centrifuge tests. The quantification of the influence of lateral boundaries in function of their type and distance to the structure is considered of importance to centrifuge modellers, allowing for optimized design of future experiments, but also to numerical modellers simulating such experiments for validation purposes.
The relevant journal publication is available here (open access):
👉 external page https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soildyn.2021.106719
More info on the specific research topic: https://geotechnics.ethz.ch/research-categories/liquefaction-structure-soil-structure-interaction.html