Dip-Slip Faulting
Recent earthquakes, such as Kocaeli (Turkey 1999), Chi-Chi (Taiwan 1999), Wenchuan (China 2008), Kaikoura (NZ 2016) and Kumamoto (Japan 2016) have shown that faulting-induced deformation can cause substantial damage to infrastructure. Until recently, little field evidence was available on the interaction of foundations and structures with a surface fault rupture. Starting with field studies after the 1999 Kocaeli and Chi-Chi earthquakes (external page J7, external page J8, external page J14), we have been studying Fault Rupture–Soil-Foundation-Structure Interaction (FR–SFSI) combining physical and numerical modelling.
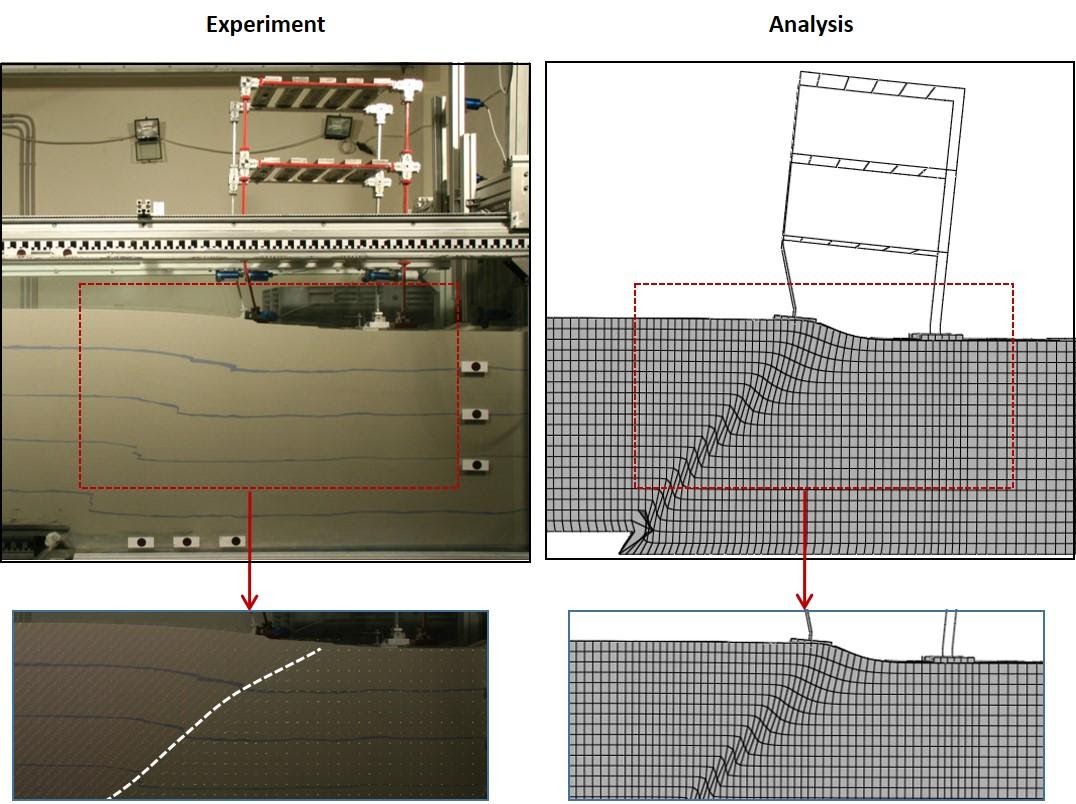
After developing and validating our numerical methods through blind Class “A” predictions of centrifuge model tests (external page J5, external page J15), we investigated the response of a variety of foundations subjected to dip-slip (normal and reverse) faulting, including shallow strip foundations (external page J18, external page J20), caisson and piled foundations (external page J32, external page J37, external page J48). Our work further extended to foundation-structure systems, including physical modelling of a 3-storey building with artificial plastic hinges (external page J101), and pipelines (external page J89). Our research culminated to the development of design methods for foundations (external page J11, external page J12, external page J26), bridges (external page J17), and tunnels (external page J10, external page J24). Our methods have been applied to a number of projects of significance (25 bridges, 8 tunnels, and several important buildings).
Selected recent publications
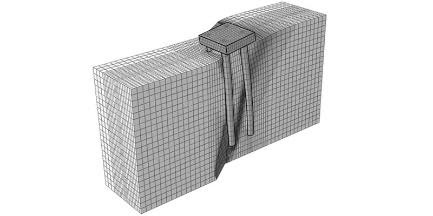
Fadaee M., Hashemi K., Farzaneganpour F., Anastasopoulos I., Gazetas G. (2020). “3–storey building subjected to reverse faulting: Analysis and experiments”, Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 138: 106297 (external page J101).
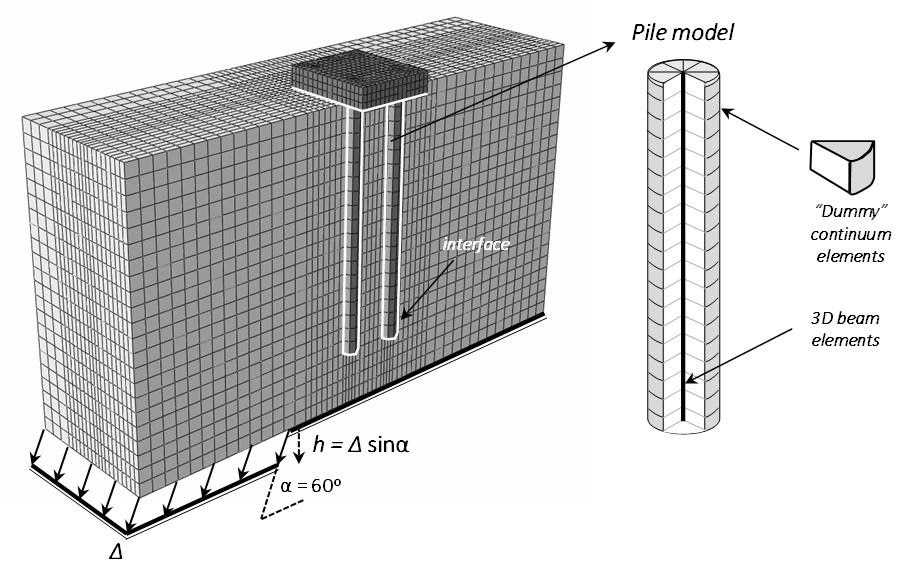
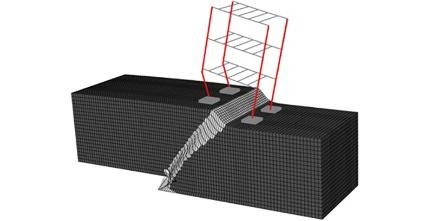
Anastasopoulos I., Kourkoulis R., Gazetas G., Tsatsis A. (2013). “Interaction of piled foundation with a rupturing normal fault”, Géotechnique, 63(12): 1042–1059 (external page J48).